Theme: COVID-19 Effect on supply of Drugs and Vaccines all over the World
Vaccines R&D 2021
Vaccines R&D 2021 looks forward to welcome all the participants across the world to attend "4th International Conference on Vaccines, Immunology and Clinical Trials" during May 13-14, 2021 which is scheduled as Webinar. The theme of our Conference is "COVID-19 effect on supply of drugs and vaccines all over the world".
Vaccines R&D 2021 meeting highlights profoundly illuminating and intelligent sessions to empower the trading of thoughts over a wide scope of controls in the field of Vaccines, Immunology and Clinical Trials. The gathering incorporates keynote talks from educated researchers, Plenary sessions, Poster Presentations, Young Researcher sessions, Symposiums, Workshop and Exhibitions. There will be open doors for those picked to introduce at the gathering to distribute an original copy dependent on their introduction in the Journal of Clinical Trials or its sister publication, Journal of Clinical Immunology and Allergy and Journal of Immunology and Immunotherapy.
Why to attend???
Vaccines R&D 2021 is intended to give an open door that with researchers from around the globe concentrated on finding out about Vaccines, Immunology and its advancements; this is the best chance to arrive at the biggest gathering of members from the Vaccines, Immunology and clinical trials network. It give an express stage to introductions, appropriate data, meet with present and potential researchers, make a sprinkle with new antibodies advancements, and get name acknowledgment at this occasion. Widely acclaimed speakers, the latest methods, improvements, and the most up to date refreshes in Vaccines, Immunology and Clinical trials are signs of this gathering.
Young Scientist Benefits
- It is a best platform for collaboration among young researchers for better development.
- Young Researchers can share their ideas with both eminent researchers and mentors.
- Our conference aims to encourage Young Researchers by honoring them with memento and certificate to the winners.
- Young Scientists will get appropriate and auspicious data by this forum.
Who can attend?
The audience who can attend for Vaccines R&D 2021 are Directors, CEOs, Presidents, Vice Presidents, Researchers, Scientists related to Vaccine R&D, Deans, Professors, Associations, Societies related to Vaccine R&D, Vaccine Developers, Vaccine Investigators, Business Entrepreneurs, Vaccine Manufacturing Companies, Vaccination Programme Organizing Government and Non-government Organizations, University Faculty, Medical Schools/Colleges, Nursing Schools/Colleges and Medical Devices Manufacturing Companies.
Track 1: Different types of COVID-19 vaccines
There are three main approaches to designing a vaccine. Their differences lie in whether they use a whole virus or bacterium; just the parts of the germ that triggers the immune system; or just the genetic material that provides the instructions for making specific proteins and not the whole virus.
- Inactivated vaccine
- Live-attenuated vaccine
- Viral vector vaccine
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 2: Benefits of getting a COVID-19 vaccine
Feeling some anxiety about receiving any new vaccine is understandable. However, while the COVID-19 vaccine was created and approved more quickly than the average vaccine, safety and testing precautions were not sacrificed to achieve effective results. COVID-19 is a highly infectious and, in some cases, highly dangerous disease. Some populations, including the elderly and persons with underlying medical conditions (i.e., comorbidities) are at greater risk for severe symptoms and even death. Natural immunity combined with vaccine-induced immunity appears to be the most effective means of safeguarding against COVID-19
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 3: Coronavirus (Covid 19) and Next-Generation Vaccines
Three new, highly transmissible variants of Covid-19 have been front and center of the news agenda in 2021. The emergence of these variants has created concern that the vaccines authorized for Covid-19 may not be the way out of the pandemic the world hoped. Fortunately, next-generation vaccines are coming through the pipeline, which has been designed with potential Covid-19 mutations and variants specifically in mind. Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses known to cause respiratory tract infections in humans and other animals. Although all viruses mutate while replicating and infecting host cells, RNA viruses are particularly unstable, meaning they are more prone to mutation during replication.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 4: Emerging and Infectious Diseases
Emerging infectious diseases are infections that have recently appeared within a population or those whose incidence or geographic range is rapidly increasing or threatens to increase soon. Emerging infections can be caused by:
- Previously undetected or unknown infectious agents.
- Known agents that have spread to new geographic locations or new populations.
- Previously known agents whose role in specific diseases has previously gone unrecognized.
- Re-emergence of agents whose incidence of disease had significantly declined in the past, but whose incidence of the disease has reappeared. This class of diseases is known as re-emerging infectious diseases.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 5: Immunization and Bioprocessing
Immunization is the process whereby a person is made immune or resistant to an infectious disease, typically by the administration of a vaccine. Vaccines stimulate the body's own immune system to protect the person against subsequent infection or disease. New bioprocess technologies such as single-use equipment and process automation open up novel possibilities for quality control and validation. This is especially important in GMP-regulated environments such as in the development and manufacturing of new influence vaccines. When facing a pandemic outbreak, the need to smoothly develop new processes and quickly scale up to clinical production volumes is key to efficiently develop new vaccinations.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 6: Human Vaccines-Infectious and Non-Infectious
A vaccine is an inactivated form of bacteria or virus that is injected into the body to simulate an actual infection. Because the injected microorganisms are 'dead,' they don't cause a person to become sick. Instead, vaccines stimulate an immune response by the body that will fight off that type of illness. It covers infectious disease targets and non-infectious disease targets. Generating vaccine-mediated protection is a complex challenge. Currently available vaccines have largely been developed empirically, with little or no understanding of how they activate the immune system. Their early protective efficacy is primarily conferred by the induction of antigen-specific antibodies. However, there is more to antibody-mediated protection than the peak of vaccine-induced antibody titers.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 7: Live Attenuated and Inactivated Vaccines
Live vaccines use a weakened (or attenuated) form of the germ that causes a disease. Because these vaccines are so similar to the natural infection that they help prevent, they create a strong and long-lasting immune response. Just 1 or 2 doses of most live vaccines can give you a lifetime of protection against a germ and the disease it causes.
Live vaccines are used to protect against:
Inactivated vaccines use the killed version of the germ that causes a disease. Inactivated vaccines usually don’t provide immunity (protection) that’s as strong as live vaccines. So you may need several doses over time (booster shots) to get ongoing immunity against diseases.
Inactivated vaccines are used to protect against:
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 8: Subunit/Conjugate and Toxoid Vaccines
Subunit, recombinant, polysaccharide, and conjugate vaccines use specific pieces of the germ—like its protein, sugar, or capsid (a casing around the germ). Because these vaccines use only specific pieces of the germ, they give a very strong immune response that’s targeted to key parts of the germ. They can also be used on almost everyone who needs them, including people with weakened immune systems and long-term health problems. Toxoid vaccines use a toxin (harmful product) made by the germ that causes a disease. They create immunity to the parts of the germ that cause disease instead of the germ itself. That means the immune response is targeted to the toxin instead of the whole germ. Like some other types of vaccines, you may need booster shots to get ongoing protection against diseases.
Toxoid vaccines are used to protect against:
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 9: Viral Vaccines and Bacterial Vaccines
Vaccines that are developed from viruses are viral. Viral vaccines contain either inactivated viruses or attenuated viruses. One of the most common examples of viral vaccine is MMR (mumps, measles, and rubella) vaccine. Inactivated or killed viral vaccines contain viruses, which have lost their ability to replicate and in turn cause disease. Bacterial vaccines contain killed or attenuated bacteria that activate the immune system. Antibodies are built against that particular bacteria and prevent bacterial infection later. An example of a bacterial vaccine is the Tuberculosis vaccine.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 10: Influenza and Respiratory Vaccines
Influenza is an acute respiratory illness that affects the upper and/or lower respiratory tract and is caused by the influenza virus, usually of type A or B. Influenza circulates continuously, causing seasonal epidemics in temperate regions and year-round epidemics in some tropical regions. Influenza viruses are continuously changing, necessitating an annual change in vaccine strains to better match with currently circulating influenza strains globally.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 11: HIV Vaccines
HIV vaccine development is complex. First attempts to develop a vaccine against HIV in the late 1980s were based on eliciting an antibody response, which is how most vaccines are thought to work. However, because HIV mutates rapidly, and its outer spike protein conceals itself from the immune system, creating the appropriate viral antigens to use in a vaccine proved remarkably difficult, and the approach was abandoned.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 12: Veterinary Vaccines and Animal Health
Veterinary vaccines have had, and continue to have, a major role in protecting animal health and public health, reducing animal suffering, enabling efficient production of food animals to feed the burgeoning human population, and greatly reducing the need for antibiotics to treat food and companion animals. Vaccination has long been an effective way to reduce disease burden in pets and farm animals and is a key tool in maintaining animal health and welfare. Vaccines continue to play an increasingly vital role in preventative health and disease control programs in animals. Innovative research and the development of safe, effective, and quality vaccines mean that our pets and farm animals continue to benefit from vital medicines that prevent or alleviate clinical signs of disease.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 13: Vaccine Safety and Efficacy
For the past two centuries, vaccines have provided a safe and effective means of preventing several infectious diseases. Although the safety of some vaccines has been questioned in recent years, the currently available vaccines are more than a millionfold safer than the diseases they are designed to prevent. Vaccines, however, should always be used in conjunction with other public health interventions. Not only are some vaccines available via injection but other vaccines are also given orally or intranasally. New vaccines are being studied for topical and intravaginal use. Also, new systems are being developed for more efficient production of vaccines, especially for influenza. Vaccines are currently available for only a limited number of viral and bacterial diseases.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 14: Vaccine Hesitancy and Health Literacy
Health literacy is defined as “the degree to which individuals have the capacity to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions.” It affects a person's ability to access and use health care, to interact with providers, and to care for himself/herself and his/her children. In particular, adults with low health literacy skills are – among other obstacles to improving health - less likely to use preventive services.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 15: Virology and Antiviral Drugs
Virology is the study of viruses and virus-like agents, including, but not limited to, their taxonomy, disease-producing properties, cultivation, and genetics. Virology is often considered a part of microbiology or pathology. During the early years of virology, this discipline was dependent upon advances in the chemical and physical sciences; however, viruses soon became tools for probing basic biochemical processes of cells. Antiviral drugs are medicines that decrease the ability of flu viruses to reproduce. When used as directed, antiviral drugs may help reduce the duration of flu symptoms in otherwise healthy children and adults and may reduce the severity of common flu symptoms.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 16: Immuno-Oncology and Immunotherapy
Our immune system is a complex network of organs, cells, and molecules that protects us from foreign substances—such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses—that can cause infection. In addition to finding and destroying foreign substances, the immune system can also locate and attack abnormal cells.
There are two main parts of the immune system:
- Innate immunity, a defense system we are born with, is the ability of the body to immediately protect itself against foreign organisms and toxins.
- Adaptive immunity is a learned defense system that develops in response to exposure to a specific foreign substance. The adaptive immune system works in one of two ways:
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that boosts the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer. It uses substances made by the body or in a laboratory to improve how your immune system works to find and destroy cancer cells Different types of immunotherapy work in different ways. Some immunotherapy treatments help the immune system stop or slow the growth of cancer cells. Others help the immune system destroy cancer cells or stop cancer from spreading to other parts of the body. Immunotherapy treatments can be used alone or combined with other cancer treatments.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 17: Vaccine Adjuvants and Antibody Engineering
Vaccine Adjuvants have been used in human vaccines for almost a century, yet very few adjuvants are licensed for human use. This has been due, in part, to a lack of understanding of their mechanism of action. However, recent insights into the innate immune system and its importance in initiating the adaptive immune response have sparked the rational design and development of the next generation of adjuvants. Several studies have validated one class of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) called Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) as vaccine adjuvant targets. Antibody engineering consists of modifying monoclonal antibody (mAb) sequences and/or structures to either enhance or dampen their functions. Monoclonal Abs have revolutionized the fields of diagnosis and immunotherapy for the treatment of a variety of diseases, particularly in cancer therapy.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 18: Animal Models and Biological Research
An animal model is a non-human species used in medical research because it can mimic aspects of a disease found in humans. Animal models are used to obtain information about a disease and its prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. By using animals, researchers can carry out experiments that would be impractical or ethically prohibited with humans. The use of animals for scientific purposes is both a longstanding practice in biological research and medicine and a frequent matter of debate in our societies. The remarkable anatomical and physiological similarities between humans and animals, particularly mammals, have prompted researchers to investigate a large range of mechanisms and assess novel therapies in animal models before applying their discoveries to humans.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
Track 19: Biomarkers and Case Reports
Vaccines prevent infectious diseases, but vaccination is not without risk and adverse events are reported although they are more commonly reported for biologicals than for vaccines. Vaccines and biologicals must undergo a rigorous assessment before and after licensure to minimize safety concerns. Potential safety concerns should be identified as early as possible during the development of vaccines and biologicals to minimize investment risk. State-of-the-art tools and methods to identify safety concerns and biomarkers that are predictive of clinical outcomes are indispensable. For vaccines and adjuvant formulations, systems biology approaches, supported by single-cell microfluidics applied to translational studies between preclinical and clinical studies, could improve reactogenicity and safety predictions.
Related Conferences:
Vaccines 2021 | Vaccines World 2021 | Immunology 2021 | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 | Immunogenetics 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 | Immune Response 2021 | Vaccine Immunology 2021 France | Vaccines & Immunization 2021 USA | Immune Response 2021 | Immunology 2021 Italy | Immunology & Immunotherapies 2021 Scotland
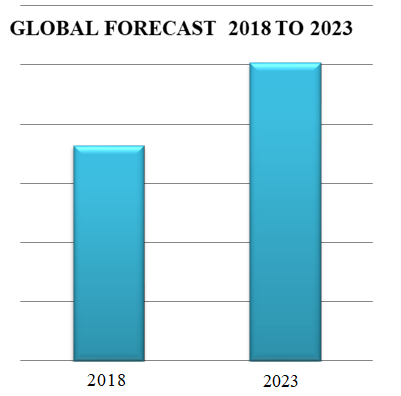
Vaccines Market Global Forecast 2018 to 2023
The market analysis of vaccines is expected to grow from USD 36.45 billion in 2018 to USD 50.42 billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2018 to 2023. Market growth have been developing due to the high prevalence of infectious diseases, growing support for vaccine R&D, investments to vaccine development and high focus on immunization. Government organizations and health care organizations have increased funding for accelerating the development of advanced infrastructure for vaccine production. The key factor for increasing market growth is a high availability of funding for vaccine R&D because it will ensure the introduction of new, advanced and effective products in the coming years.
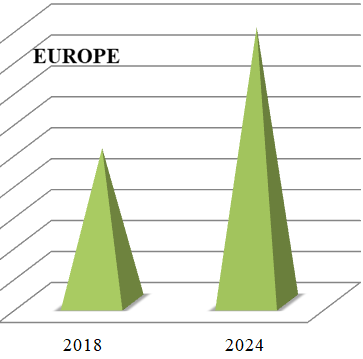
European Vaccine Market Size and Growth (2019-2024)
Vaccines market in Europe is estimated at $9.99 Billion in 2019 and is assured to reach $17.83 billion by 2024 with an annual growth rate of 12.28%. Due to more number of Cancer and HIV cases the market rate of vaccine has been increased. World Health Organization(WHO) estimate that the vaccine market value will increase up to almost 17.83 billion in 2023, due to arrival of new therapeutic preventive and adult vaccines.
Conference Highlights
- Coronavirus (Covid 19) and Next Generation Vaccines
- Emerging and Infectious Diseases
- Immunization and Bioprocessing
- Human Vaccines-Infectious and Non Infectious
- Live Attenuated and Inactivated Vaccines
- Subunit/Conjugate and Toxoid Vaccines
- Viral Vaccines and Bacterial Vaccines
- Influenza and Respiratory Vaccines
- HIV Vaccines
- Veterinary Vaccines and Animal Health
- Vaccine Safety and Efficacy
- Vaccine Hesitancy and Health Literacy
- Virology and Antiviral Drugs
- Immuno-Oncology and Immunotherapy
- Vaccine Adjuvants and Antibody Engineering
- Animal Models and Biological Research
- Biomarkers and Case Reports
- Different types of COVID-19 vaccines
- Benefits of getting a COVID-19 vaccine
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | May 13-14, 2021 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Clinical Trials
- Journal of Clinical Immunology and Allergy
- Journal of Immunology and Immunotherapy
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



